산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 성능평가 기준 연구
Performance Evaluation Criteria for Safety Helmets of Forest Firefighting Crews
Article information
Abstract
산불진화대원의 안전 확보와 작업능률 향상을 위해 안전헬멧에 대한 성능평가 기준을 개발하였다. 산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 기준이 현재 국내에 없기 때문에 한국소방산업기술원(KFI)에서 운용중인 소방대원용 헬멧에 대한 기준을 기초로 하여 연구를 시작하였다. 관계자 의견 수렴 및 외국 기준의 검토를 통하여 26개 시험항목 중 15개 시험항목을 제외하고 11개 시험항목을 선정하였다. 2 종류의 일반 안전헬멧과 하나의 소방대원용 헬멧을 시료로 하여 KFI 기준을 적용하여 시험하고 그 결과를 비교하였다. 시험 결과 일반 안전헬멧은 착장체와 턱끈의 기능이 기준에 미달하였고 특히 PE나 ABS 재질은 열에 취약함을 확인하였다. KFI 기준과 ISO 16073, NFPA 1977, NFPA 1971 및 BS EN 443의 판정기준을 비교하여 우리나라 산불진화대원들의 작업 환경에 적합한 11개의 시험항목과 판정기준을 최종 선정하였다.
Trans Abstract
To secure the safety and improve the work efficiency of forest firefighting crews, performance evaluation criteria for safety helmets were developed in this study. Because the standards for forest firefighting safety helmets are not available in Korea, we began our study based on the standards for firefighting safety helmets used by the Korea Fire Institute (KFI). Eleven test items were selected excluding 15 other items out of the 26 test items that, through the consultation of stakeholders and the review of foreign standards, were initially included in our study. Two types of general safety helmets and one firefighting helmet were tested by applying KFI standards, and the results were compared. The general safety helmets did not meet the standards of the retention system and chin strap. Additionally, polyethylene and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene materials were found to be especially weak under heat conditions. We compared the criteria of KFI, International Standardization Organization (ISO) 16073, National Fire Prevention Association (NFPA) 1977, NFPA 1971, and British Standards European Norm (BS EN) 443, and finally selected 11 test items and their acceptance criteria suitable for the work environment of forest firefighting crews in Korea.
1. 서 론
산림청의 산불관리통합규정 안전수칙에는 산불진화대원에게 안전장비를 최대한 지급하여야 한다고 규정하고 있다[1]. 이에 따라 각 자치단체에서는 산불진화 안전장비 13종을 지정하여 산불진화대원들에게 보급하고 있다.
국내에는 산불 진화용 헬멧이 별도로 지정되어 있지 않기 때문에 산불진화대원들은 일반 안전헬멧을 사용하고 있다. 한 지방자치단체에서 산불진화용 안전장비를 구매하기 위해 제시했던 규격서에는 안전헬멧의 재질을 ABS로 지정하고 야광 좌우 반사테를 사용하라는 것이 요구사항이었다. 산불진화대원의 안전과 제품의 품질 관리를 위해서는 안전헬멧의 성능을 명확하게 제시할 필요가 있다.
산불진화대원의 인명 피해 방지와 작업 효율 향상을 위해서는 개인보호장비에 대한 표준 규격이 반드시 필요하다. 이번 연구에서는 산불진화대원의 주요 업무 및 작업 환경에 대한 검토를 거친 후, 산불진화대원의 필수 보호 착용도구 중 안전헬멧에 대한 성능평가 기준을 제안하고자 하였다. 여기서 기준이란, 어떤 품목에 대해 성능 평가방법과 적합․부적합 판정 방법을 규정한 것을 말한다.
2. 시험 항목 선정
2.1 KFI 기준(소방용 진압헬멧의 KFI 인정기준)
산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 기준이 현재 국내에 없기 때문에 한국소방산업기술원(KFI)에서 운용중인 「소방용 진압헬멧의 KFI 인정기준」 [2]을 기초로 하여 연구를 시작하였다. 산불진화대원이든 소방대원이든 작업 현장에서 부상을 방지하고 작업효율을 향상시키기 위한 목적으로 개인보호장비를 사용하기 때문에 개인보호장비가 갖추어야 할 요구사항들은 비슷하다. 그러나 산불진화대원과 소방대원은 주요 업무와 작업 환경이 많이 다르기 때문에 차이점들을 고려하여 시험항목들을 선정해야 하며 성능에 대한 요구 수준에도 차이를 두어야 한다.
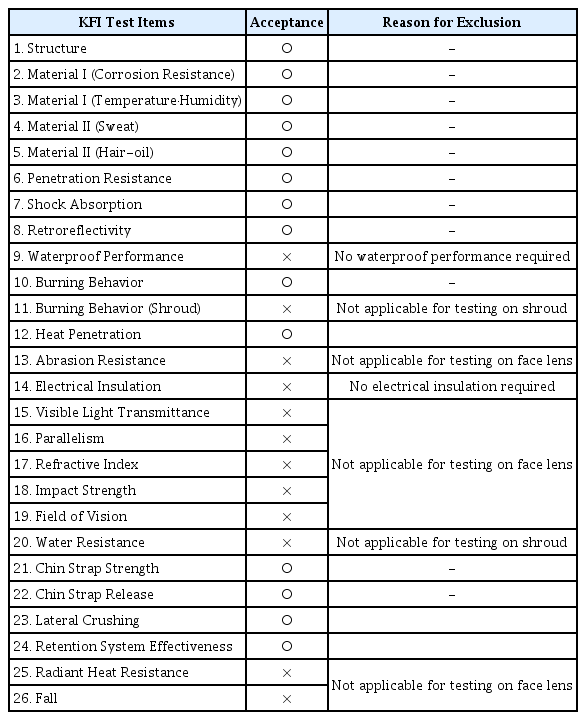
「소방용 진압헬멧의 KFI 인정기준」에 있는 26개의 시험항목을 기본으로 하여 관계자(산불진화대원) 의견 수렴 및 자료 검토를 통하여 관계가 없는 시험항목들을 걸러내었다. 소방용 헬멧의 안면렌즈, 물받이와 관련된 시험들은 해당이 없기 때문에 제외하였다. 그리고 산불 진화작업에서 전기절연과 완전한 방수성능까지는 필요하지 않기 때문에 관련 시험항목들을 제외하였다. 이렇게 26개 시험 항목 중 12개 시험항목을 제외하고 14개 시험항목을 1차로 선정하였다. 그 결과를 Table 1에 나타내었다.
2.2 국내외 기준 비교 및 시험항목 선정
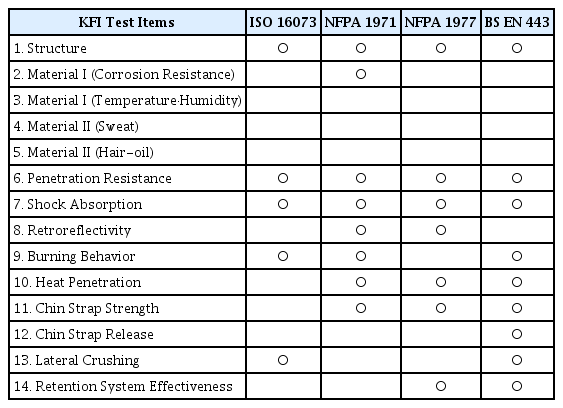
산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 시험항목을 선정하기 위해 2차로 외국의 기준에 있는 시험항목들을 검토하였다. 검토한 외국 시험기준들을 Table 2에 나타내었다. ISO 16073 [3]과 NFPA 1977 [4]은 산불과 관련된 개인보호장비에 대한 기준이고 NFPA 1971 [5]과 BS EN 443 [6]은 건축물 화재와 관련된 개인보호장비에 대한 기준이다.
1차로 걸러진 14개의 시험항목들과 외국 기준들의 시험항목을 비교하여 Table 3에 나타내었다. 재료에 대한 온도ㆍ습도 시험, 땀 시험 및 두발유 시험은 다른 외국기준에서 찾아볼 수 없었다. 따라서 이 3개 시험항목을 제외한 11개 항목들을 산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 시험항목으로 선정하였다.
3. 시 험
2 종류의 일반 안전헬멧과 하나의 소방대원용 헬멧에 대해 KFI 기준을 적용하여 시험하고 그 결과를 비교하였다. 앞에서 선정된 11개 시험항목 중에서 구조, 내식성, 반사성능 시험을 제외하고 나머지 8가지 항목에 대해 시험하였다.
산불진화대원용 안전헬멧의 구조는 고용노동부의 보호구 안전인증 고시에서 규정하고 있는 헬멧에 대한 기준[7]을 적용하였다. 내식성 시험은 금속 재질이 있는 경우에만 적용하는 시험이므로 생략하였다. 반사성능 시험은 헬멧에 부착되는 형광 반사체의 반사성능을 측정하는 것이기 때문에 산불진화대원용과 소방대원용을 구별할 필요가 없으며 기존의 KFI 기준을 그대로 적용해도 무방하다.
3.1 시료
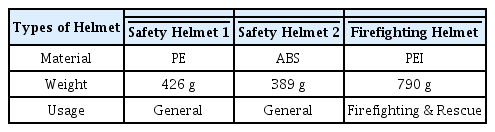
시험에 사용된 3가지 안전헬멧에 대한 특성을 Table 4에 나타내었다. 일반용 안전헬멧은 PE (Polyethylene)와 ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) 재질이며 소방 구조용 헬멧은 PEI (Polyether imide) 재질이다. PEI는 열보호 성능이 우수한 반면 가격이 비싸다. 일반용 안전헬멧은 불에 약한 스티로폴이 충격 흡수제로 사용되어서 가볍기는 하지만 산불진화용으로는 적합하지 않다. 소방 구조용 헬멧은 충격 흡수제 재질이 PE이다. 소방 구조용 헬멧은 무게가 약 790 g으로 일반 안전헬멧에 비해 무게가 약 2배 정도 무겁다.
3.2 시험 방법
KFI에서 운용중인 「소방용 진압헬멧의 KFI 인정기준」 [2]에서 정한 시험방법과 판정기준을 8개의 시험항목에 적용하여 실시하였다. 각 시험방법과 판정기준은 시험결과에 요약하여 나타내었다.
4. 결과 및 고찰
4.1 내관통성 시험
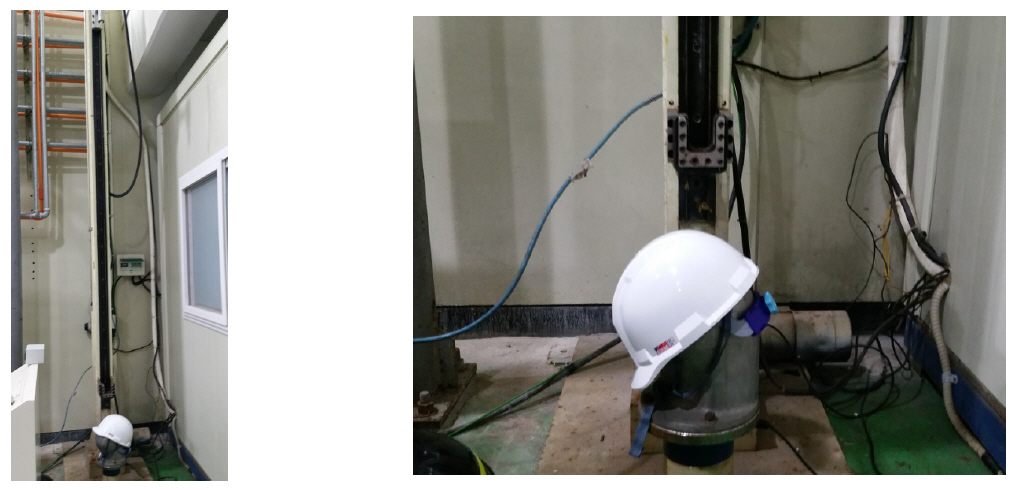
내관통성 시험은 0.45 kg의 철제 추를 3 m 높이에서 헬멧에 자유낙하시켜 관통거리를 측정하는 시험이다. 이 시험은 헬멧의 앞, 뒤, 좌, 우 측면 및 윗면에 대해 실시하여 모두 기준을 충족하여야 적합 판정을 받는다. 시험 장면을 Figure 1에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 5에 나타내었다. 3 종류의 헬멧 모두 앞, 뒤, 좌, 우, 윗면에 대해 관통거리가 9.5 ㎜ 이하로 측정되어 적합 판정을 받았다.
4.2 충격흡수성 시험
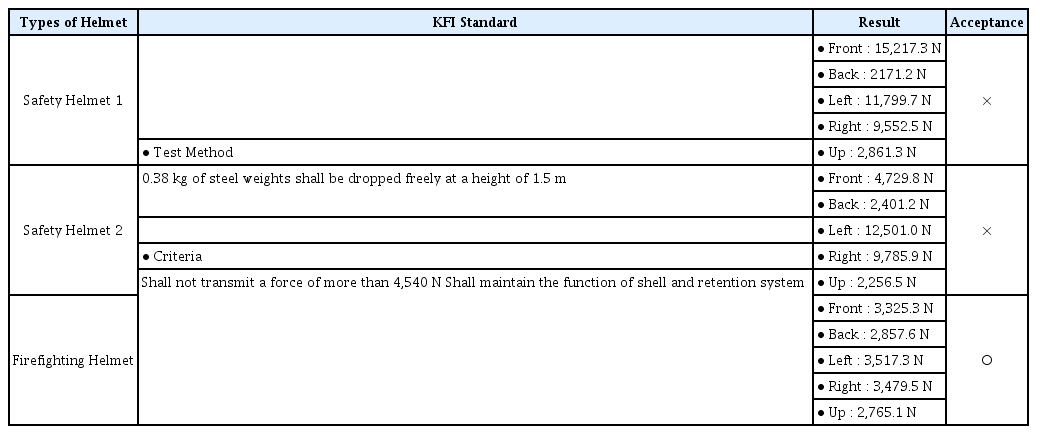
충격흡수성 시험은 3.58 kg의 철제 추를 1.5 m 높이에서 헬멧에 자유낙하시켜 충격력을 측정하는 시험이다. 이 시험도 헬멧의 앞, 뒤, 좌, 우 측면 및 윗면에 대해 실시하여 모두 기준을 충족하여야 적합 판정을 받는다. 시험 장면을 Figure 2에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 6에 나타내었다. 일반 안전헬멧은 2개 모두 최고 전달 충격력이 4,540 N을 초과한 경우가 있기 때문에 부적합 판정을 받았으며 소방구조용 헬멧은 적합 판정을 받았다.
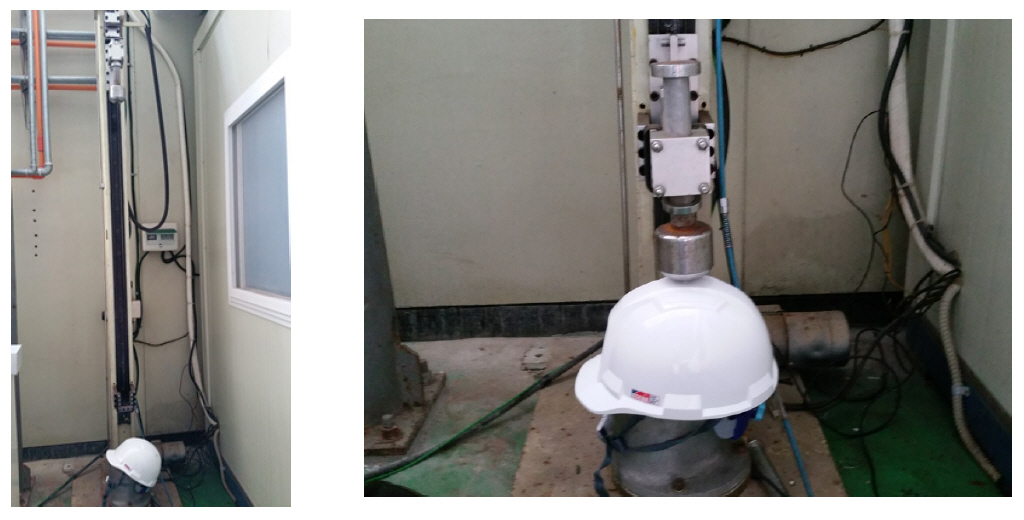
4.3 난연성 시험
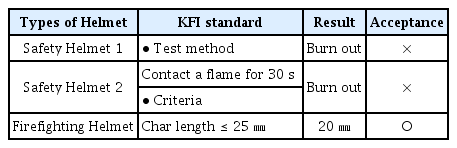
난연성 시험은 헬멧 시편에 30초간 불꽃 접촉을 한 후 탄화길이를 측정하는 시험이다. 시험 장면을 Figure 3에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 7에 나타내었다. 일반 안전헬멧은 2개 모두 불에 완전히 타버려 부적합 판정을 받았으며 소방 구조용 헬멧은 탄화길이가 25 ㎜ 이하로 측정되어 적합 판정을 받았다.
4.4 내열성 시험
내열성 시험은 헬멧을 260 ℃의 항온조에 5분간 노출시켜 열변형이 생기는지 여부를 판정하는 시험이다. 시험 장면을 Figure 4에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 8에 나타내었다. 일반 안전헬멧은 2 개 모두 Figure 4에서 보는 바와 같이 전체가 용융되어 부적합 판정을 받았으며 소방 구조용 헬멧은 열변형이 발생하지 않아 적합 판정을 받았다.
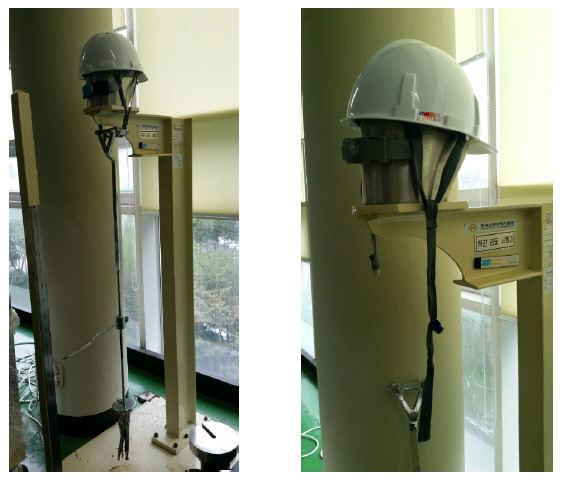
4.5 턱끈 강도 시험
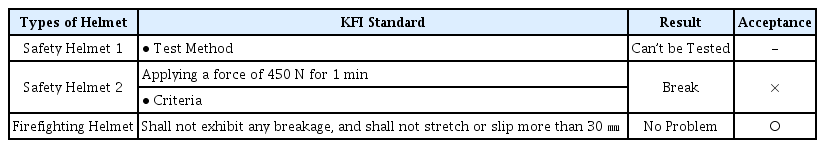
턱끈강도 시험은 턱끈에 450 N의 하중을 1분간 가하여 턱끈이 떨어지거나 손상이 생기는지 여부를 판정하는 시험이다. 시험 장면을 Figure 5에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 9에 나타내었다. 일반 안전헬멧 1은 턱끈에 하중을 걸 수 없는 구조여서 시험이 불가하였다. 일반 안전헬멧 2는 턱끈이 모체에서 탈착되어 부적합 판정을 받았다. 소방구조용 헬멧은 어떠한 이상도 발견되지 않아 적합 판정을 받았다.
4.6 턱끈 풀림 시험
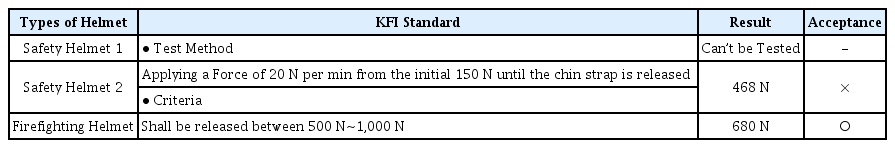
턱끈풀림 시험은 초기 150 N의 하중에서 턱끈이 풀어질 때까지 분당 20 N의 하중을 턱끈에 가하여 턱끈이 풀어지는 하중을 측정하는 시험이다. 시험 장면을 Figure 6에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 10에 나타내었다. 일반 안전헬멧 1은 턱끈에 하중을 걸 수 없는 구조여서 시험이 불가하였다. 일반 안전헬멧 2는 468 N의 하중에서 턱끈이 풀어져서 부적합 판정을 받았다. 소방 구조용 헬멧은 680 N의 하중에서 턱끈이 풀어져서 적합 판정을 받았다.
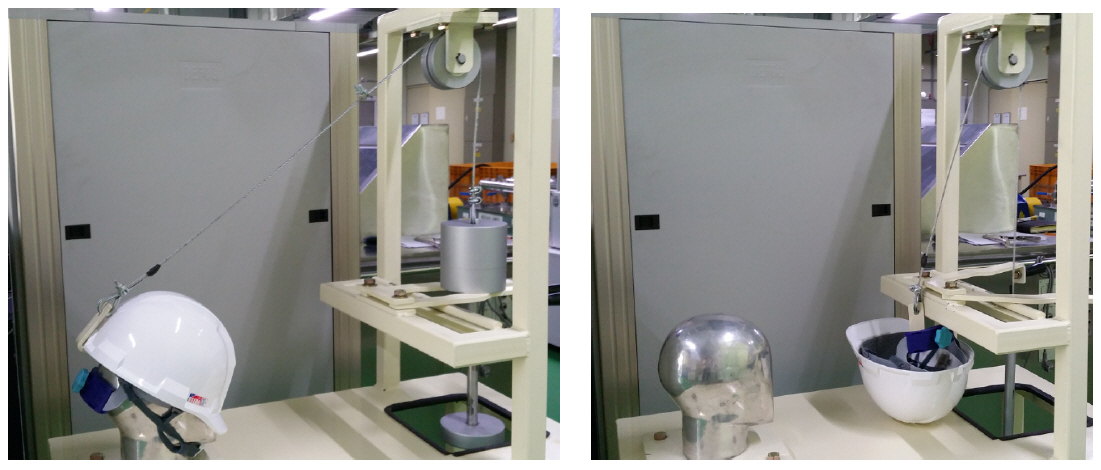
4.7 측면변형 시험
측면변형 시험은 평행판 사이에 헬멧을 놓고 분당 100 N의 하중으로 430 N이 될 때까지 헬멧에 하중을 가하고 30초간 유지하여 헬멧이 변형되는지 여부를 판정하는 시험이다. 시험 장면을 Figure 7에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 11에 나타내었다. 일반 안전헬멧은 최대 측면변형이 각각 62 ㎜, 67 ㎜로 측정되어 모두 부적합 판정을 받았다. 소방 구조용 헬멧은 최대 측면변형이 29 ㎜, 잔여 변형이 2 ㎜로 측정되어 적합 판정을 받았다.
4.8 이탈 시험
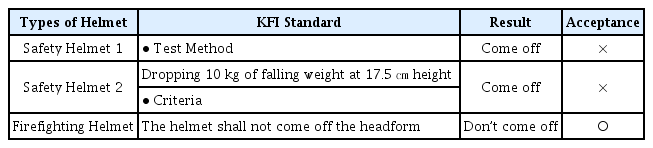
이탈 시험은 헬멧을 머리 모형에 고정시키고 17.5 ㎝ 높이에서 10 kg의 추를 헬멧에 낙하시켜 헬멧이 벗겨지는지 여부를 판정하는 시험이다. 시험 장면을 Figure 8에 나타내었고 시험 결과를 Table 12에 나타내었다. 일반 안전헬멧은 2개 모두 벗겨져서 부적합 판정을 받았으며 소방 구조용 헬멧은 헬멧이 벗겨지지 않아 적합 판정을 받았다.
4.9 고찰
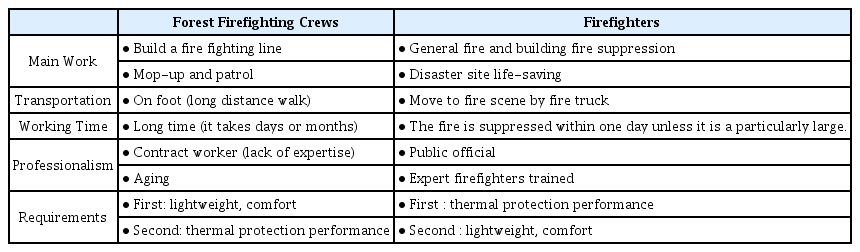
앞에서 산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 시험 항목을 11개로 선정하였다. 이어서 산불진화대원의 작업 환경과 안전에 대한 요구사항을 고려하여 11개 시험항목에 대한 판정기준을 정하여야 한다. 일반적으로 일반 개인보호장비에 대한 기준보다 소방대원용 개인보호장비에 대한 기준이 더 엄격하다. 한국소방산업기술원에서는 소방대원용 개인보호장비에 대한 기준을 운용하고 있으나, 그 기준을 산불진화대원용 개인보호장비에 그대로 적용하기에는 무리가 있다. 소방대원과 산불진화대원의 업무 특성 및 환경에 차이가 있기 때문이다. Table 13에 산불진화대원과 소방대원의 업무특성을 비교하여 나타내었다[8].
산불진화대원은 산불에 맞서 직접 진화하기보다는 방어선 구축, 잔불 정리 및 뒷불 감시가 주요 임무이다. 산불은 그 특성상 진화작업이 장기화되는 경우가 많으며, 산불진화대원은 장거리를 도보로 이동해야 하기 때문에 장비의 경량성과 쾌적성이 우선적으로 요구된다. 반면 소방대원은 화재 현장까지 소방차를 타고 이동하여 현장에서 직접 화재 진압을 해야 하므로 장비의 열보호성능이 우선적으로 요구된다. 소방대원은 공무원으로서 훈련을 통해 숙달된 전문 화재진압 대원임에 비해 산불진화대원은 대부분 계약직이고 고령화로 인해 작업에 대한 전문성이 떨어지므로 장비의 경량성에 대한 요구는 더 크다[9].
산불진화대원들은 현재 일반용 개인보호장비를 사용하고 있다. 잔불 정리와 뒷불 감시가 주요 업무라 하더라도 산불 현장에선 항상 불의 위험에 노출되어 있기 때문에 일반용 개인보호장비로는 안전에 대한 요구 조건을 충족시킬 수 없다. 따라서 소방용 장비의 성능까지는 아니더라도 일반용 안전장비보다는 성능 수준이 높은 새로운 성능평가기준을 찾고자 하였다.
2 종류의 일반용 안전헬멧과 하나의 소방 구조용 안전헬멧에 대해 KFI 인정기준의 시험 방법에 따라 8개 항목의 시험을 수행한 결과를 Table 14에 나타내었다. Table 14에서 보는 바와 같이 PE와 ABS 재질의 일반 안전헬멧은 내관통성 시험 1개 항목에서만 적합 판정을 받은 반면, 소방 구조용 안전헬멧은 8개 시험항목에서 모두 적합 판정을 받았다.
산불진화대원용 안전헬멧도 어느 정도의 열에는 견딜 수 있도록 재질을 개선할 필요가 있음을 확인하였다. 또한 충격에 견딜 수 있고 안정적인 착용을 위해서는 모체와 착장체의 구조 및 턱끈의 기능을 개선할 필요가 있음을 확인하였다.
안전헬멧에 대한 성능시험의 판정기준을 검토하기 위하여 앞에서 시험했던 항목들에 대해 KFI 기준과 외국의 기준들을 비교하여 Table 15에 나타내었다. ISO 16073과 NFPA 1977은 산불진화대원용 개인보호장비에 관한 기준이고 NFPA 1971과 BS EN 443 기준은 소방대원용 개인보호장비에 대한 기준이다. 열보호 성능과 열에 대한 내구성 관련 시험들은 소방대원과 산불진화대원의 작업환경이 다르기 때문에 판정기준에 차이가 있어야 한다. 따라서 판정기준에 차이가 있을 경우 ISO 16073과 NFPA 1977 기준을 우선적으로 수용하였다. 그러나 안전헬멧의 기계적․물리적 내구성 관련 시험들은 소방대원과 산불진화대원 간의 판정기준에 크게 차이를 둘 필요가 없다.
Table 15를 참조하여 산불진화대원용 안전헬멧의 성능평가 판정기준을 선정하였다. 내관통성 시험, 충격흡수성 시험, 난연성 시험에 대해서는 산불진화대원용 개인보호장비에 대한 기준인 ISO 16073을 수용하였다. 내열성 시험의 경우 다른 기준들은 260 ℃에서 5분간 노출하는데 비해 BS EN 443 기준은 90 ℃에서 20분간 노출하는 조건이었다. 산불진화대원들은 주불 진화보다는 잔불 진화가 주요 업무이고 또한 장시간 작업을 하기 때문에 BS EN 443 기준을 수용하였다. 턱끈강도 시험의 판정기준은 산불진화대원용 개인보호장비에 대한 기준인 NFPA 1977을 수용하였다. 턱끈풀림 시험과 이탈 시험은 KFI와 BS EN 443에서만 적용하고 있는데 판정기준이 동일하므로 KFI 기준을 그대로 수용하였다. 측면변형 시험도 KFI와 ISO 16073 및 BS EN 443 기준이 동일하므로 KFI 기준을 그대로 수용하였다.
5. 결 론
산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 기준이 현재 국내에 없기 때문에 산불진화대원의 안전 확보와 작업능률 향상을 위해 산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 성능평가 기준을 제안하고자 하였다. 한국소방산업기술원(KFI)에서 운용중인 「소방용 진압헬멧의 KFI 인정기준」의 26개 시험항목을 기초로 하여 연구를 시작하였다. 그러나 산불진화대원과 소방대원은 주요 업무와 작업 환경이 많이 다르기 때문에 관계자(산불진화대원) 의견 수렴 및 외국 기준의 검토를 통하여 26개 시험항목 중 15개 시험항목을 제외하고 11개 시험항목을 선정하였다.
소방용 안전헬멧에 대한 성능평가 기준을 산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 그대로 적용하기에는 요구 수준이 너무 높은 반면, 일반 안전헬멧은 산불 진화용으로 사용하기에 품질이 부족하다. 따라서 소방용 안전헬멧의 성능까지는 아니지만 일반 안전헬멧보다는 성능이 우수하고 산불 진화작업에 적합한 성능 수준을 찾기 위해 산불진화대원들이 사용하고 있는 2 종류의 일반 안전헬멧과 하나의 소방대원용 헬멧을 대상으로 KFI 기준을 적용하여 시험하고 그 결과를 비교하였다.
시험 결과 산불진화대원용 안전헬멧도 어느 정도의 열에는 견딜 수 있도록 재질을 개선할 필요가 있음을 확인하였다. 또한 충격에 견딜 수 있고 안정적인 착용을 위해서는 모체와 착장체의 구조 및 턱끈의 기능을 개선할 필요가 있음을 확인하였다. 이어서 판정 기준을 수립하는데 참고하기 위해 KFI 기준과 ISO 16073, NFPA 1977, NFPA 1971 및 BS EN 443의 판정기준을 비교하여 우리나라 산불진화대원들의 작업 환경에 적합한 판정기준들을 최종 선정하였다.
산불진화대원용 안전헬멧에 대한 11개의 성능평가 시험항목 및 판정기준을 Table 16에 나타내었다. 안전헬멧의 구조는 고용노동부의 보호구 안전인증 고시에서 규정하고 있는 헬멧에 대한 기준을 적용하였다. 내관통성 시험, 충격흡수성 시험, 난연성 시험은 ISO 16073 기준을, 내열성 시험은 BS EN 443 기준을, 턱끈강도 시험은 NFPA 1977 기준을 그리고 내식성 시험, 반사성능 시험, 턱끈풀림 시험, 측면 변형 시험 및 이탈 시험은 KFI 기준을 적용하였다.
Acknowledgements
본 연구는 국립산림과학원의 지원을 받아 수행되었으며 관계제위께 감사드립니다.